Our Team
Our long history of unparalleled commitment to partnering with the most extensive carriers and our
ability to offer the most versatile services
ability to offer the most versatile services

Full Name
“Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec.”

Full Name
“Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec.”

Full Name
“Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec.”

Full Name
“Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec.”
Fulfillment Center vs Warehouse: Which is best suitable for your Business
Technological improvements and the growing demand for more accuracy and efficiency are driving a significant revolution in the warehousing business. This change is bringing about a revolution in the way warehouses function, spurring the deployment of cutting-edge technologies and inventive equipment. We’ll explore the newest developments and trends that are changing the warehousing scene in this article, from sophisticated automation and robots to the incorporation of cloud computing and Internet of Things devices. Through investigating these advancements, we may acquire a thorough comprehension of how these technologies are augmenting operational efficacy, refining inventory management, and satisfying the dynamic requirements of the contemporary supply chain.
Robotics and Automation
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
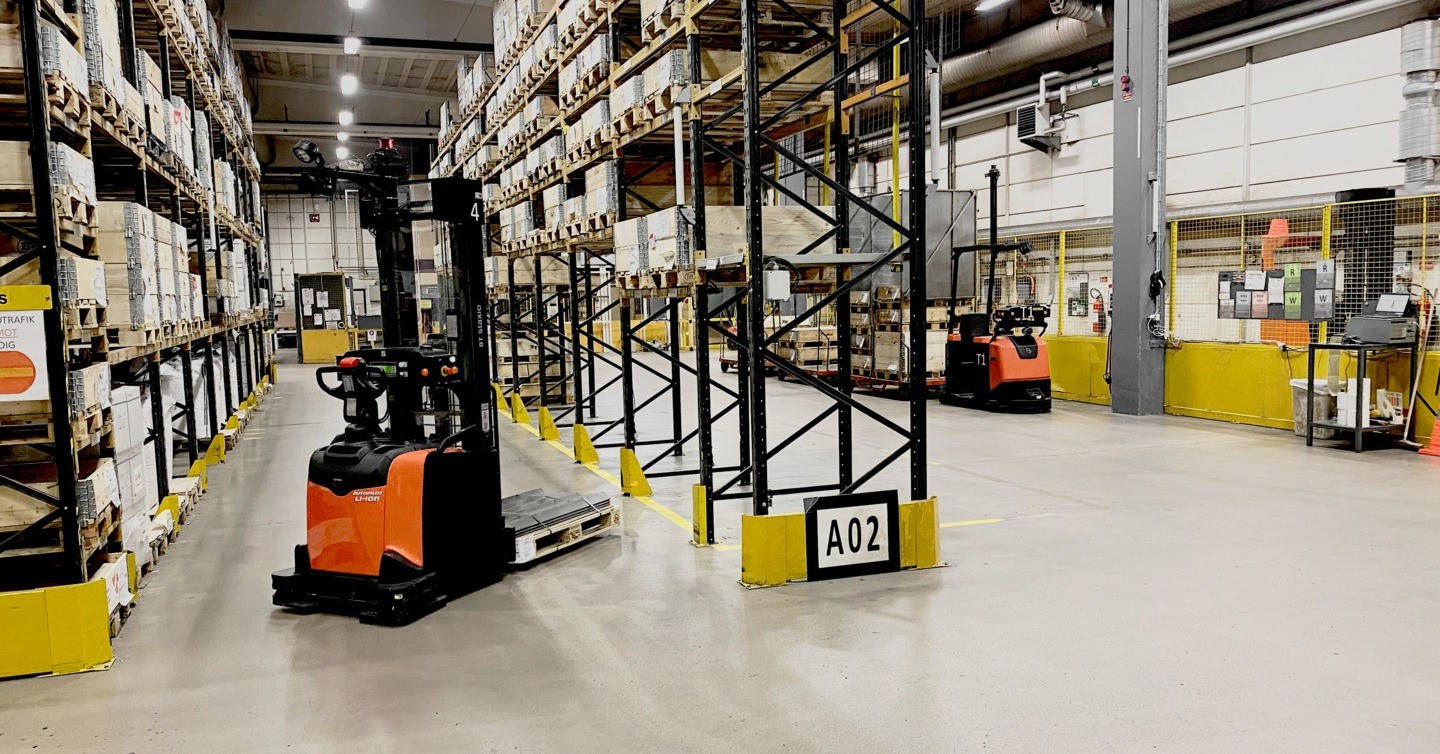

Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are mobile robots that use wires or markers buried in the floor to follow pre-programmed routes. They might also make use of cutting-edge navigational tools like lasers or vision magnets. AGVs are mostly utilised for material transportation in manufacturing facilities and warehouses in industrial settings. They greatly increase production by automating the transportation of goods. This minimises mistakes and cuts down on human labour. AGVs are capable of performing activities including pallet handling and towing unit load transportation. They are necessary for contemporary, highly effective warehouses.
Articulated Robotic Arms
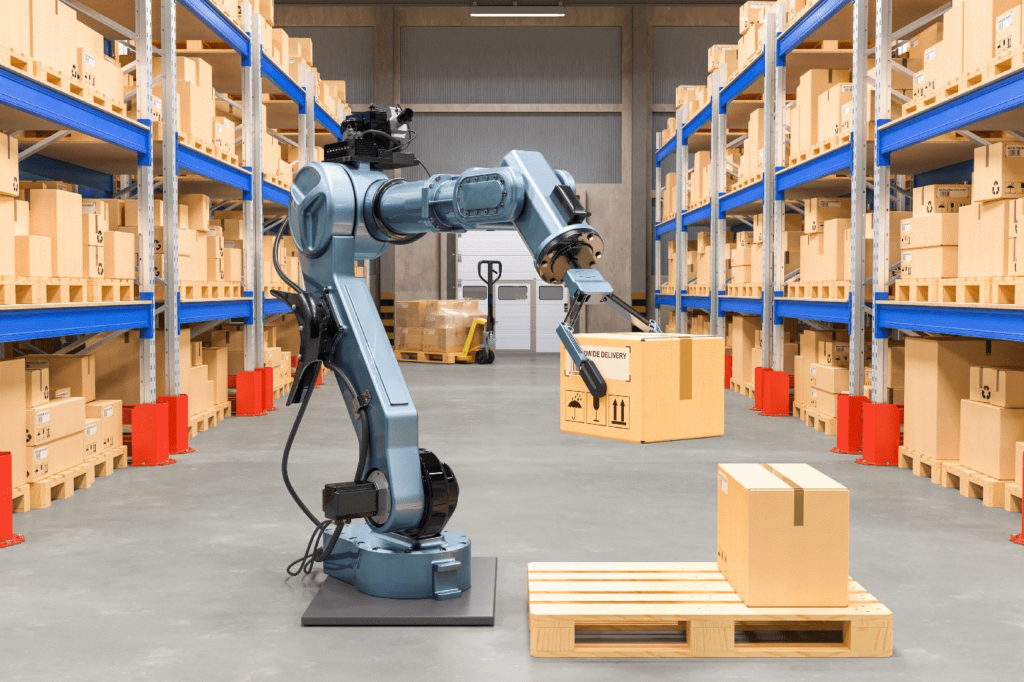

Robots with articulated limbs are multifunctional devices. They are made for jobs that need a great deal of speed and precision. These robotic arms are capable of numerous tasks. Palletizing, packing, and selecting are all included in this. They are perfect for difficult assembly chores or sorting processes because of their multi-jointed limbs, which allow them to reach and maneuver in complex patterns. Their accuracy is further improved by the incorporation of AI and sophisticated sensors. As a result, they may operate with other automated systems in the warehouse and handle fragile objects.
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
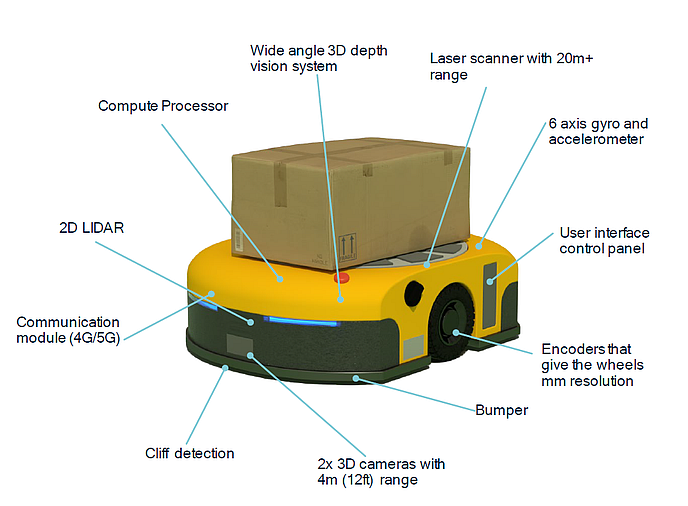
Warehouse robots of the most recent generation are called Autonomous Mobile Robots, or AMRs. As opposed to AGVs, AMRs make use of advanced onboard sensors and navigation systems. They comprehend and make sense of their surroundings. This enables them to navigate on their own. They dynamically modify their courses and dodge impediments. AMRs are capable of handling jobs like carrying items, checking inventories, and restocking supplies with efficiency because they are made to work alongside human workers. In contemporary warehouses, their adaptability and capacity to function securely in changing conditions make them indispensable.
Drones

Drones are revolutionizing inventory and asset management within warehouses. With cameras, barcode scanners and RFID readers, drones can fly through aisles for quick, accurate scans. This capability drastically reduces the time required for inventory counts. It also enhances asset tracking. Overall, efficiency improves significantly. Additionally, drones can access hard-to-reach areas. They provide a comprehensive view of inventory levels and conditions. This helps in maintaining accurate records and improving inventory management.
Cloud Technologies
Cloud-based warehouse management systems (WMS) are becoming more and more popular. It is anticipated that the growth of these solutions would surpass that of conventional on-premise software. Cloud-based WMS provide many benefits. This offers improved scalability and real-time inventory visibility. They also boost the effectiveness of operations. Businesses may access their warehouse data from any location by utilising the cloud, which improves collaboration and decision-making. Furthermore, additional features like predictive analytics and the ability to integrate with other supply chain technology are frequently included in cloud solutions. These characteristics improve warehouse operations even further.
Internet of Things (IoT)
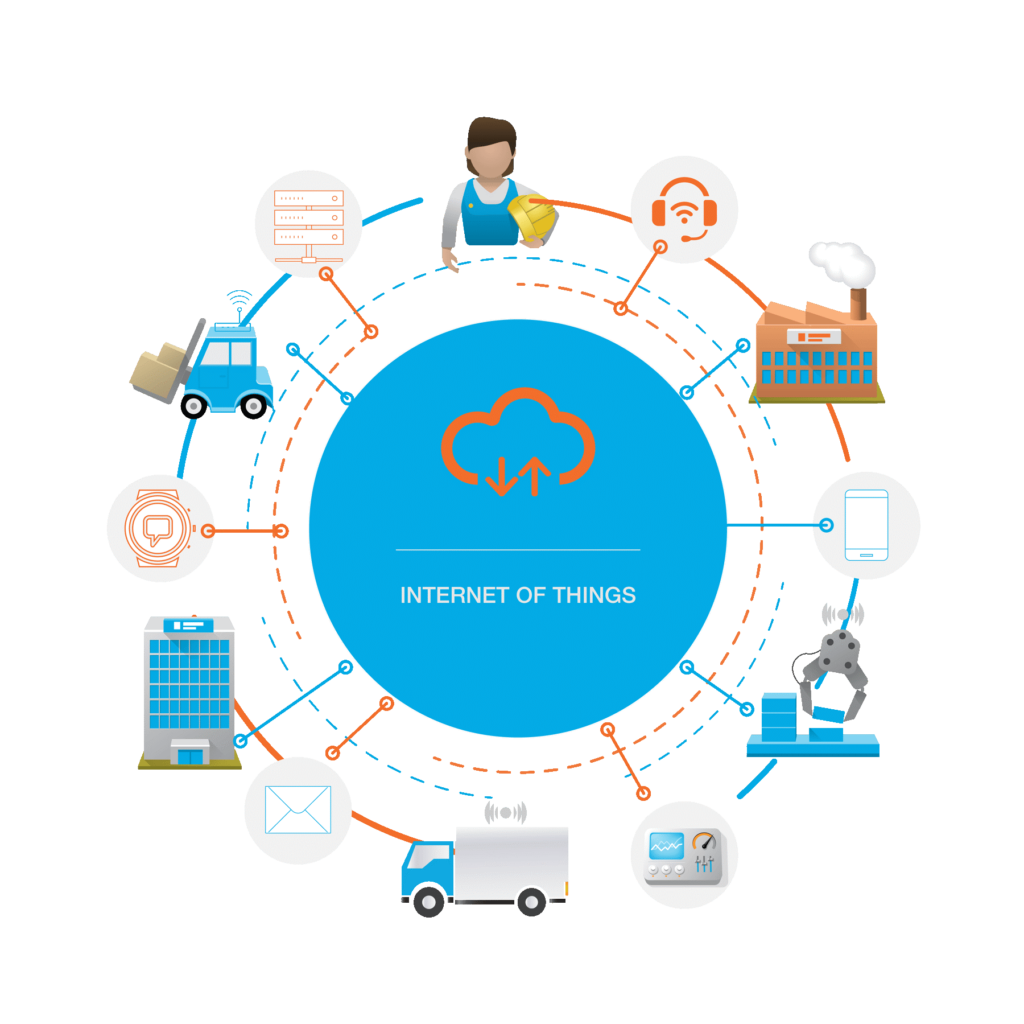
IoT devices like sensors and smart tags are transforming warehouse operations by providing real-time monitoring and data collection. These devices can track the condition of goods. This includes temperature, humidity and location. As a result, products are stored and handled properly. For example, IoT sensors can alert warehouse managers if a shipment of perishable goods exceeds a specific temperature threshold. This allows for immediate corrective action. This level of monitoring helps prevent spoilage. It reduces waste and enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring that products remain in optimal condition throughout the supply chain.
3D Printing
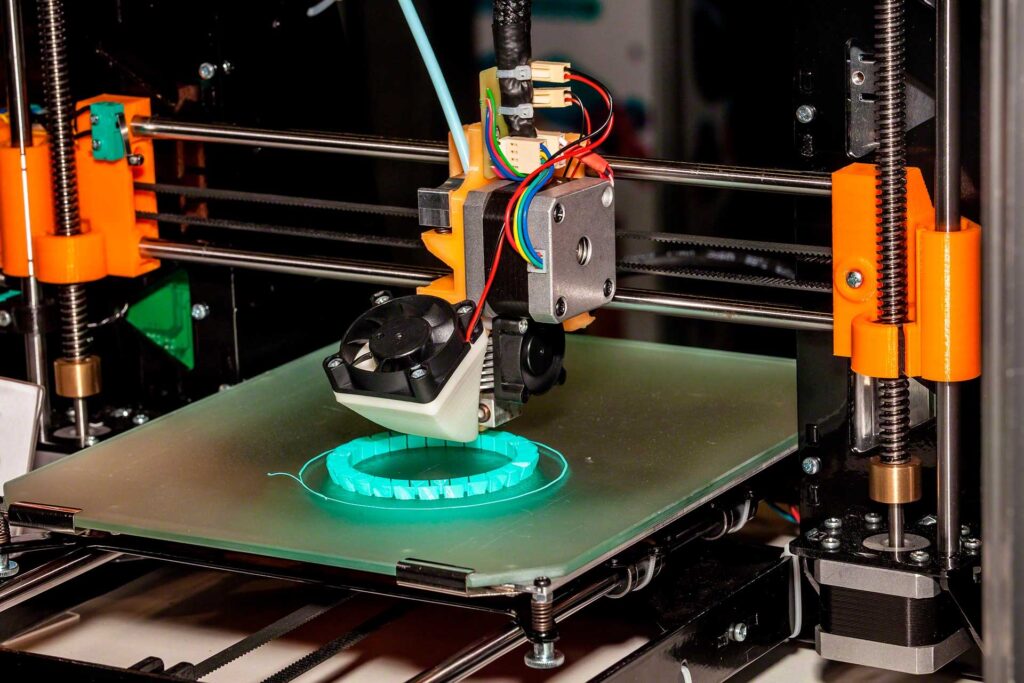
Traditional supply chain paradigms are about to be disrupted by 3D printing. Direct on-demand production within the warehouse is made possible by it. Thanks to this technology, companies may now manufacture customised items and parts near the point of consumption. Significant savings are realised in lead times and shipping expenses. For example, a warehouse that has 3D printers installed can produce machine spare parts. In accordance with client requirements, it may also produce customised goods. More versatility is provided by this. Furthermore, it enhances responsiveness to market demands.
On-Demand Warehousing
An inventive concept called “on-demand warehousing” offers companies adaptable storage options. Long-term commitments are frequently necessary for traditional storage contracts. On the other hand, on-demand warehousing enables businesses to adjust their storage capacity in response to changes in demand. Businesses that experience seasonal swings would especially benefit from this flexibility. It is also helpful in cases of unforeseen increases in demand. Through the utilisation of on-demand warehousing, businesses can maximise their storage expenses. They make sure they have the resources available to meet consumer needs without going overboard.
RFID Tagging
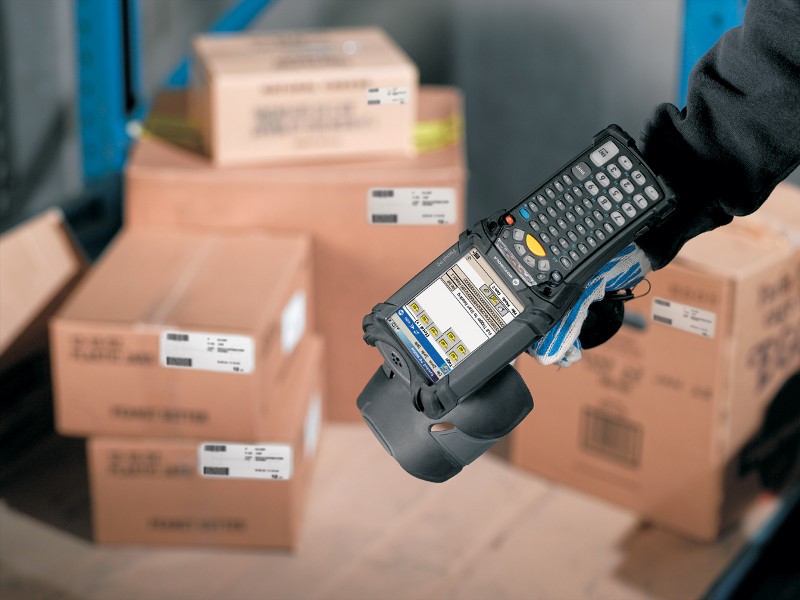

RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tagging is a sophisticated method of asset and inventory tracking in a warehouse. RFID tags have a reading range that is greater than that of conventional barcodes. Line of sight must not be direct. Inventory management is sped up by this capacity. It’s possible to scan several RFID tags at once. This improves precision. Movement of goods is tracked more effectively. The use of RFID technology lowers human error. It offers up-to-date information on inventory levels. Improved control over operations and streamlined warehousing processes are made possible by technology.
Conclusion
Warehouses may dramatically save operating costs, optimise workflows, and raise service standards by utilising these technology developments, all of which raise customer happiness. Robots reduce human error and increase throughput by automating repetitive operations. Real-time data from IoT devices enables proactive management and maintenance. Cloud computing improves coordination and decision-making throughout the supply chain by providing scalable warehouse management systems. Because it enables on-demand production, eliminates the need for big stocks, and saves storage expenses, 3D printing completely transforms inventory management.
The warehousing sector will be essential to meeting the demands of a market that is changing quickly and supporting the global supply chain as long as the industry innovates. Warehouses must adopt these developments in order to lead the way in operational excellence and establish new benchmarks for responsiveness and efficiency. The future is here. Warehouses may stay competitive and able to satisfy the changing needs of the market by implementing these technologies and putting themselves at the forefront of the sector.
Interested in working with Lean SCS?
We are not only 3PL company we provide end to end supply chain solutions.
LEAN
SUPPLY CHAIN SOLUTION
North Office
- 630, JMD Megapolis, Sector 48, sohna Road, Gurugram, Haryana 122018
- 8800906084
- info@leanscs.in
West Office
- Arcadia Building NCPA Marg, Nariman Point, Mumbai, Maharashtra 400021
- 9717234777
- info@leanscs.in
North Office
- 630, JMD Megapolis, Sector 48, sohna Road, Gurugram, Haryana 122018
- 8800906084
- info@leanscs.in
West Office
- Arcadia Building NCPA Marg, Nariman Point, Mumbai, Maharashtra 400021
- 9717234777
- info@leanscs.in
OUR Services
Menu








